According to the World Bank, small businesses represent about 90 percent of all global businesses and more than 50 percent of the global workforce. In addition, SMEs in emerging and formal markets create 7 out of 10 jobs.
Although their cumulative contribution is small compared to larger global enterprises, they help create new work opportunities, contribute to increasing the tax base and development, improve local and national economies, and are a powerhouse for innovation.
In essence, small businesses keep economies running.
So, is it not strange that we rarely come across incredible small business growth stories? What’s holding them back?
Multiple research studies on small business growth (and failure) over the last three decades have attributed these to factors such as regulations, economic conditions, technology, and access to business expertise.
However, one common theme among these is that most small businesses lack growth strategies to ensure sustained performance over a long period.
Growth strategies are crucial for all businesses, small and large.
Without a growth strategy, your business and sales team will, in all probability, only react to changing market conditions and not be prepared to ride the wave or grow sustainably.
Myth 1 – “Businesses, other than healthcare, cannot grow during a recession.”
This is what small business growth strategies are for. They can help-
- Create strategic alliances
- Work on business culture to improve productivity
- Rework marketing strategies
The Benefits of Growth Strategies for Small Businesses
- Survive external risks like market volatility and inflation
- Become more sustainable in the long-run
- Increase revenue generation
- Gain a greater competitive advantage
- More leeway in capital strength for reinvestment
- Reach new customers and markets
- Grow your brand and influence
While small businesses do face deeper resource constraints in comparison to large enterprises, they possess agility which helps in implementing growth strategies easily.
To this end, this article will focus on the top 4 growth strategies to help small businesses commit to ambitious growth.
Top 4 Small Business Growth Strategies
 Top 4 Small Business Growth Strategies
Top 4 Small Business Growth Strategies1. Innovation, Development, and Commercialization Strategy
Innovation is where your business ideates and converts them into innovative solutions to deliver value to your target audience.
Hence, innovation comes in many shapes and sizes such as-
 Innovation, Development, and Commercialization Strategy
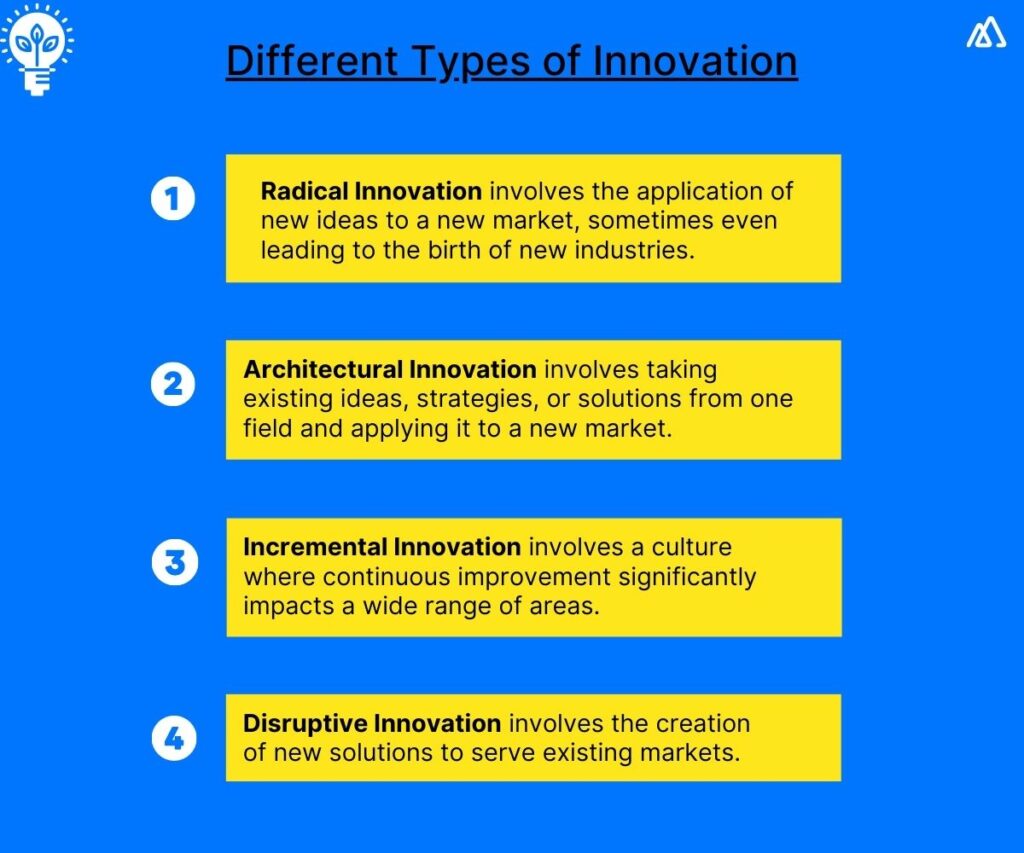
Innovation, Development, and Commercialization Strategya) Radical Innovation
Radical innovation involves the application of new ideas to a new market, sometimes even leading to the birth of new industries.
Famous examples – John Deere with tractors, Netflix with online-only entertainment
b) Architectural Innovation
Architectural innovation involves taking existing ideas, strategies, or solutions from one field and applying it to a new market.
Famous examples – IBM with multi-core processor, Benz with an internal combustion engine
c) Incremental Innovation
Incremental innovation involves a culture where continuous improvement significantly impacts a wide range of areas.
Famous examples – KLM Airlines with commercial aviation, Proctor and Gamble with a synthetic detergent
d) Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation involves the creation of new solutions to serve existing markets. As the markets already exist, practical solutions can be better tested for scalability.
Famous examples – Airbnb with collaborative revenue generation, Aldi with discount stores
In essence, ideation is the generation and communication of the originality of thought and innovation is the selection of the right business ideas, refining them, and exercising their implementation into the business.
Regardless, small businesses must commercialize innovation to realize profits.
Commercialization is an attempt by a business to gain profit from innovation. They can do so by-
- Incorporating innovation into products, processes, and services
.
.
- Sell the innovation and/or patent to a third party
To be successful, businesses must-
- Run ideation sessions and finalize a list
- Identify the right innovation and do market research
- Built and test a prototype or a blueprint
- Identify the value chain and scalability probabilities
- Determine investments and risks involved
- Identify and setup product/service development process
- Find the right commercialization strategy
Myth 2 – “Innovation development is too expensive, difficult, and risky for a small business.”
Innovation is the cornerstone of industry progress. Small businesses can work on ideation and innovation within the organization to keep R&D costs low. They can-
- Improve existing offerings
- Add new features or services to existing offerings
- Partner with a business entity for innovation development
2. Accessing New and Unmet Revenue Generation Pools
 Accessing New and Unmet Revenue Generation Pools
Accessing New and Unmet Revenue Generation PoolsRevenue generation is the successful conversion of value offered by a business to its customers into money. Accessing new and unmet revenue generation pools can be done by reconfiguring existing revenue models or implementing new ones.
The focus then moves to revenue streams (sources of income). A business may have one or more sources of income.
It is common that businesses to stay put in current markets and focus on improving or amending existing revenue generation strategies to keep things simple.
Types of revenue generation strategies include-
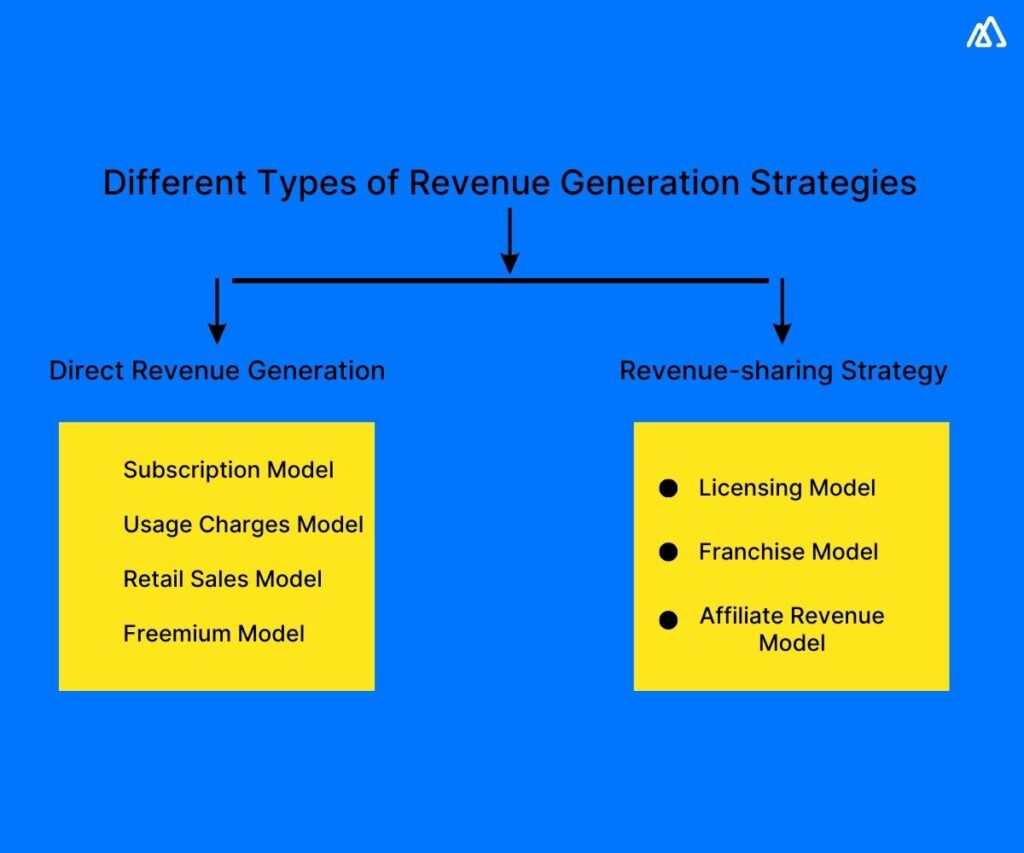
a) Direct Revenue Generation
This is where a business handles all sales aspects whereby revenue streams flow directly from the source to them.
Famous examples – Microsoft with Windows operating system, AT & T with post-paid mobile network
Subtypes include-
The Subscription Model is where customers pay a recurring price at regular intervals, like month to month or quarter to quarter, for products or services.
Famous examples – Microsoft with Windows operating system, AT & T with post-paid mobile network
The Usage Charges Model or transaction-based revenue generation is where customers pay per use or pay for bulk or time-limited use.
Famous examples – Viacom with a pay-per-view pricing model for boxing exhibitions, McAfee, and Intel with Anti-virus security for Windows
The Retail Sales Model is where the business sets up retail stores where the products are kept for sales or services rendered.
Famous examples – Starbucks chain of coffeehouses, Barnes & Noble for a bookstore chain
The Freemium Model is where the basic products are free, but users must pay for additional features and functions, customization, etc.
Famous examples – Trello with online project management, Spotify with online music.
b) Revenue-sharing Strategy
This is where a business outsources, fully or partially, its revenue generation to a third party. In effect, the third party is compensated from the revenue generated, predefined as a business agreement partnership.
Subtypes include-
The Licensing Model is where users are permitted to use products, services, patents, or brands in exchange for licensing fees. This is usually per-use or time-based.
Famous examples – Nestle licenses Starbucks products, Marvel licensed Spider-Man to Sony Picture Entertainment
The Franchise Model is similar to licensing but the difference is that entities can use the parent company’s branding and marketing strategies. The parent company earns revenue by allowing multiple entities to offer its product or service to customers.
Famous examples – KFC restaurants, Hilton hotels & resorts
Channel Partner Sales or the affiliate revenue model, is where partners or resellers sell your product or render services on your behalf.
Famous examples – Cisco Channel Partner Sales for telecommunications and more, PayPal’s partner program for payments
To be successful, businesses must-
- Gather market and customer data
- Make a list of revenue models best suited to your business
- Map an implementation plan
- Ensure you communicate the change in revenue streams to your existing customers
- Use metrics to measure progress and make changes accordingly
Myth 3 – “We have no way to improve our cash flow situation.”
The preservation of business stability is paramount. However, in volatile markets, it is more important to invest in growth than trying to conserve depleting reserves. They can-
- Change their pricing strategies
- Offer promotions, discounts for upselling, cross-selling, and referral programs
- Focus on multiple-level engagement for relationship development with digital marketing
- Partner with other businesses (JV and M&A)
- Ask suppliers to extend credit
- Be insured against a cashflow crisis (rarely used as it is an expensive undertaking)
3. Investing in Strategic Partnerships (Including Funding)
 Investing in Strategic Partnerships (Including Funding)
Investing in Strategic Partnerships (Including Funding)A commonly used growth strategy, strategic partnerships can help expand capabilities without the hassles of investing in in-house talent and assets. In addition, businesses can reduce risks, perform efficiently, and adapt faster to changing market scenarios.
Strategic partnerships can come in many shapes and sizes. Here’s a breakdown of the 2 broad models:
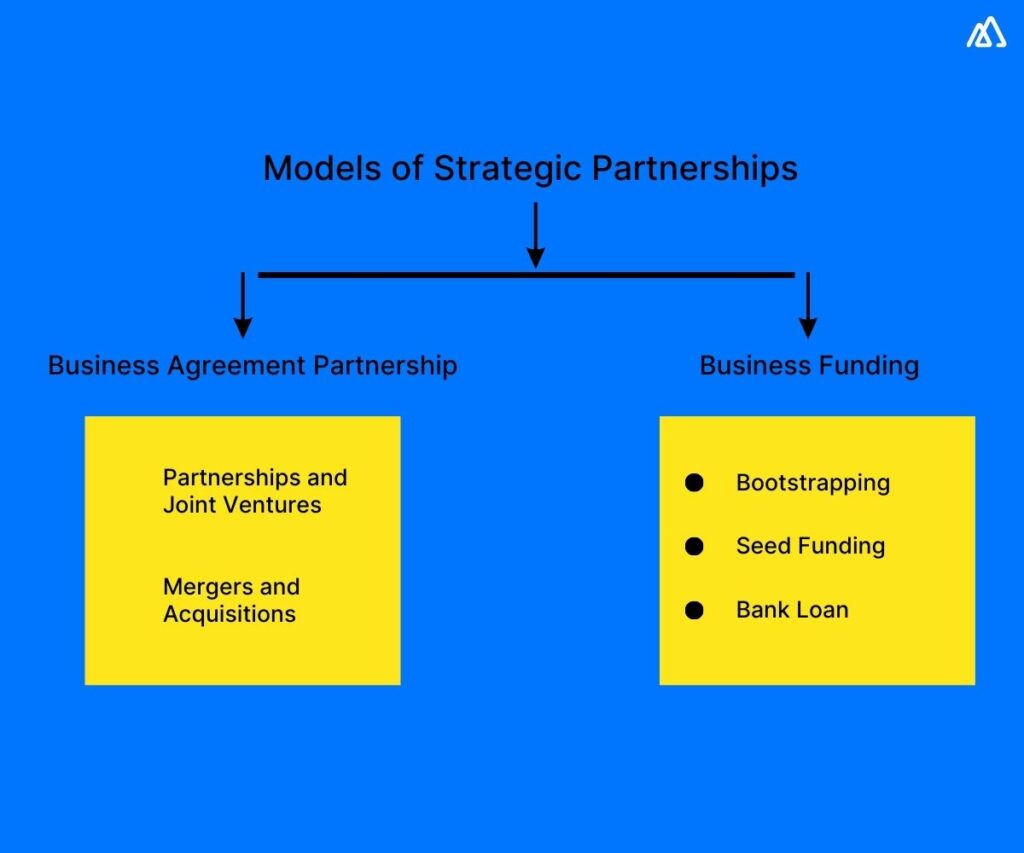
a) Business Agreement Partnership
Business agreements are where two or more entities come to a legally binding agreement to create an independent business entity that will work towards a collective set of goals.
They may agree to share resources, assets, technology, and profits to extend their capabilities.
Common types of strategic partnerships include-
Partnerships and Joint Ventures (JV) – Joint ventures are structured partnerships set up for contractual agreements to pool resources, assets, talent, and products/services towards a specific goal.
–
In a JV, a small business can partner with another business entity to create a completely new business entity to expand its capabilities.
Famous examples – Sony and Ericsson for telecommunications, Microsoft healthcare intelligence products with General Electric GE health-related technologies to form Caradigm
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) – is where two businesses come together to form a single company. While mergers, also known as ‘mergers of equals, are where two companies come together as one, acquisitions are where one company takes over another into its fold.
Famous examples – Google’s acquisition of Android, the merger between Exxon and Mobile
b) Business Funding
Small businesses are often low on capital and their growth plans are contingent on their financial situation. Today, small businesses have access to multiple options to fund their business plans and growth strategies.
Common funding and investment types include-
Bootstrapping – Scrape together capital by selling personal assets, applying for low-interest government loans, or borrowing from family and friends to fund your plans.
Famous examples – Amazon Studios TV and film production, Pebble Technology Corp. with consumer electronics like smartwatches
Seed Funding – The trend of the decade, seed funding is where an enterprise looks for investors by selling equity or getting into business ventures. Seed funding is categorized based on the required capital and track records.
Famous examples – GGV Capital invested in Airbnb and Slack, Sequoia Capital invests in Indigo Paints, SoftBank invested in OlaCabs and WeWork
Bank Loan – Probably the preferred model in this list, bank loans are offered on revenue generation capacity, helping small businesses overcome hurdles such as time to generate investments and credits.
To be successful, businesses must-
- Identify gaps in access to the partner’s resources
- Conduct research into markets, customer segments, and requirements, and an analysis of their competitors.
- Identify expansion areas, geographies, and other related values that the strategic partner can bring to the table
- Define a plan with the partner including responsibilities and make it legal Monitor their performance
Myth 4- “Banks have turned me down. I have run out of alternative funding options.”
Opting for investments and funding is the new norm. The reasoning behind this is “As long as my innovation and revenue generation strategy is sound, I will find any investor. This is a better option than taking out a bank loan or selling my assets.”
Funding alternatives include-
- Put the idea out there for seed funding
4. Market Penetration and Expansion
 Market Penetration and Expansion
Market Penetration and ExpansionMarket Penetration
This strategy focuses on existing products or services and growing the business in the current market. What makes this strategy different from point 2 is its approach of taking on competitors head-on.
–
In other words, the focus shifts to attracting customers by implementing strategies relative to strategies employed by the competition.
Common market penetration strategies include-
- Offer products/services at a lower rate than your competition.
- Offer better promotions, discounts, and referral incentives than your competition.
- Improve existing product/service features to attract attention.
- Approach your competition’s distributors with better offers.
- Advertise aggressively – online and traditional.
- Expand your distribution channels into your competitor’s territory.
Famous examples – Reliance Jio with telecommunications, Dollar Shave Club with grooming products
Market Expansion
Here, businesses expand into new geographies and target new customer segments to sell current products/services. They do so with innovation or foraying into markets where direct competition for their existing products/services is not high.
–
Famous examples – Facebook with social media applications, Under Armour with apparel and sports equipment
Common market expansion strategies include-
- Adding more distribution channels in new geographies.
- Opening new retail stores in new locations and territories.
- Acquisitions are where the business acquires another business entity. Thereby, instantly increasing marketability and their customer base.
- Diversification is where new features are added to existing offerings or new products/services are introduced to new markets. Diversification can be an offshoot of innovation or an acquisition of a business entity.
To be successful, businesses must-
- Identify and research the markets
- Take cognizance of their stock and production/service capacity
- Finance their plans and accept all risks
- Address marketing strategies per target audience
Myth 5 – My business doesn’t need to restructure its management as it grows.
As such, an orientation towards growth dictates that management be restructured not just to improve planning and operations, but also to try to address difficulties that its employees face.
Essentially, a restructuring exercise means facilitating change by bringing in talent who are unbiased. While hiring consultation firms or individual consultants can be an expensive affair, it is not a standard.
External facilitators can focus on-
- Improving existing business processes like employee feedback
- Implementing new technology like sales CRM
- Helping transition to new strategies like pricing
- Create new departments like digital marketing
How to Grow Your Business Quickly?
 How to Grow Your Business Quickly?
How to Grow Your Business Quickly?Regardless of what business you run, you want to make sure that your business keeps flourishing. But it is not a matter of a short while. Growing a business is an ongoing process and asks for hard work, patience, and a smart approach that keeps your business running. So, let’s take a look at a few tips that you can use to give your business the best chance at growing.
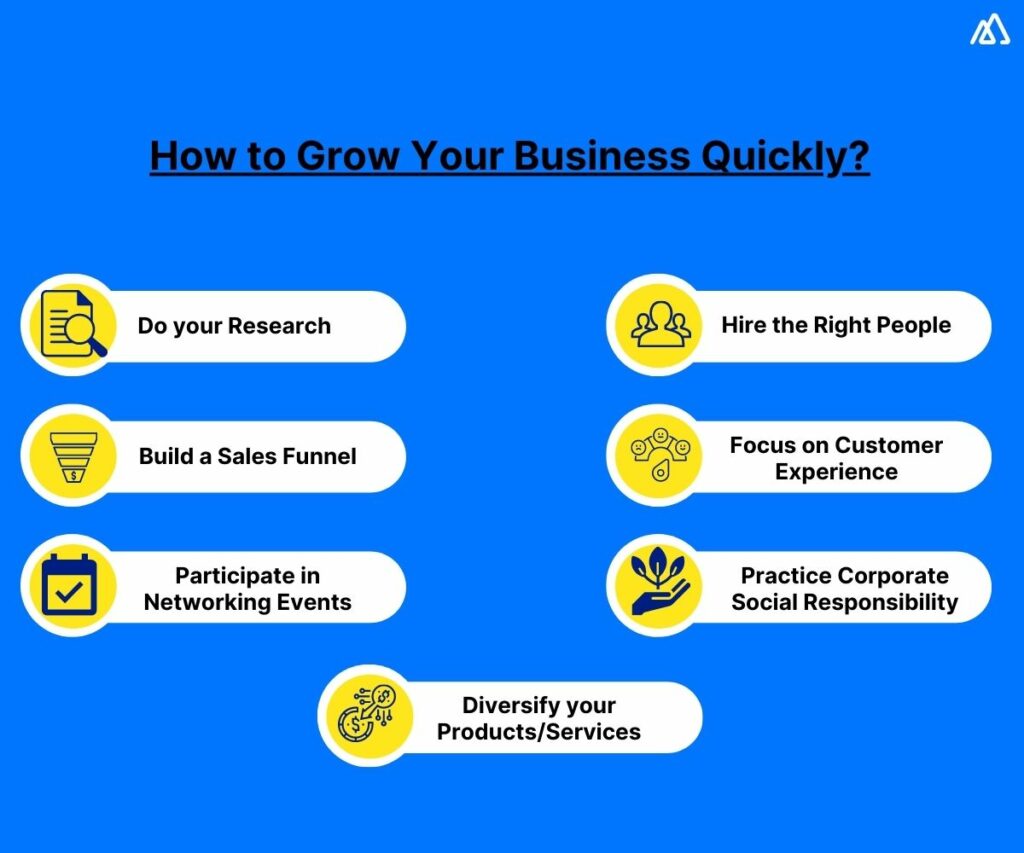
1. Do your Research
Market research doesn’t only help you understand your existing customers but also your potential customers. It’s necessary to gain insight into your target market and get well-versed in their needs. This will help you determine how you can grow your business and make changes to meet those needs. In addition to this, research your competitors, their strengths, and their weaknesses to drive your decisions on how you can scale your business.
2. Hire the Right People
Before you expect your business to grow, you must make sure that you have the right team to achieve your business goals. When your employees are dedicated and work towards the common goal, your business stays on track and continues growing. Moreover, by assigning the tasks to be done to the right people, you can free up your time and energy, and focus on tasks that help you take your business to new boundaries.
3. Build a Sales Funnel
The sales funnel is the customer’s journey with your business. When they make an entry into your business, they are at the top of the funnel. When they buy something or sign up for a service, they have successfully gone through the funnel. As a business, it’s your responsibility to move your customers through the funnel to make a sale. You can get send them updates on your business, offer discounts, or contact them often to fuel their interest in your business.
4. Focus on Customer Experience
What your customers talk about your business can make or break your business. While working on delivering the best services/ products to your business, you must also focus on delivering quality experiences to make them praise your business on social media and other websites. If you mess it up, they will tell the world even faster. Both your current and potential customers must be happy. Improving your ways of customer retention can work wonders for you.
5. Participate in Networking Events
Networking events are a great way of connecting with people in your industry and increasing your brand visibility. Such events give you a chance of being spotted by new customers and grow your business. Such relationships can be beneficial for you for years to come. So, check local professional organizations to know about upcoming events and spread the word about your business. Make use of the opportunity to meet other business owners, speak as an industry expert, or promote your business through a booth setup.
6. Practice Corporate Social Responsibility
A lot of customers these days are more interested in brands that match their own values. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) means you know how your business impacts the community. When you show people what your business is doing to positively impact the community, you automatically win customers. For instance, running a green business shows the public that you don’t want your business to harm the environment.
7. Diversify your Products/Services
Undoubtedly, you want to sell your main product or service to your customers. But offering different products and services can help you get new customers for your business. You can do this by researching the market and finding out if there is something that you can offer your customers to buy or you can find ways of offering your existing products.
Fostering Small Business Growth
Small businesses are vital for the global economy and deliver bottom lines of employment, contribute to increasing the tax base and development, and are a key source of innovation.
Growth strategies for small businesses can help them overcome their lack of access to resources and create long-time value generation for their customers.
All of this, coupled with the right Sales CRM, can help small businesses compete with bigger businesses and thrive even in bullish markets. We hope this article can help you foster the necessary growth for your small and growing business.